Sailboat Parts
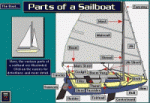
Backstay – The (usually wire) cable from the stern to the masthead, helping support the mast.
Ballast – The weight in a sailboat’s keel (sometimes in a centerboard) that helps keep the boat from heeling too much.
Boom – A horizontal pole (or spar), joined to the mast by a gooseneck, to which the foot of the sail is attached.
Boom Vang – A tackle (leverage system using ropes and blocks) secured to the boom and the deck that prevents the boom from lifting.
Bow – The forward (or front) of boat.
Centerboard – A thin keel-like structure that can be raised (usually rotated on a hinge up into a centerboard trunk in the hull); present on many sailboats without a fixed keel to prevent the boat from being blown sideways. On a larger boat, a keel (usually permanent) is used.
Clew – The lower rear corner of a sail.
Cleat – A fitting around which a line is secured.
Cockpit – The well in a boat’s deck, usually found aft (near the stern) from which the crew operates the boat.
Deck – The floor of a boat; a platform which covers or extends horizontally across a boat.
Fairlead – A fitting or block which is used to change the angle of a sail’s sheet, usually a jib, to improve its sail trim.
Foot – The bottom edge of a sail (compare to leach and luff).
Forestay – The (usually wire) cable from the bow to the masthead, helping support the mast. <
strong>Forward – Toward the bow.
Gooseneck – The fitting that attaches the boom to the mast.
Halyard – Line or wire used to hoist a sail.
Hull – The body of the boat.
Jib – The triangular sail attached to the forestay.
Jib Sheet – The sheet which controls the trim of the jib.
Leech – The back edge of a jib or mainsail.
Mainsail – The Mainsail is a fore and aft sail which is set to the afterside of the mainmast.
Mainsheet – The sheet which controls the trim of the jib.
Mast – A vertical pole (or spar) on a sailboat which supports rigging and sails. The mainmast supports the mainsail.
Shroud – The length of standing rigging ( that doesn’t move) that runs from the top of the mast to the starboard (right) and port (left) side of the boat and stabilizes the mast.
Stern – The after part (or rear) of the boat.
Thwart – A seat that runs cross sides on a small boat.
Tiller – The steering device of a sailboat. On larger boats, a wheel is used. Also known as the helm.
Topsides – The sides of a sailing vessel from the waterline to the deck.
Transom – The flat surface at the stern (or rear) of the boat.
Traveler – A track located at the stern of the boat that runs from port to starboard used to control the mainsheet.
Sea Knot Terms
Belay – To make one line tight around a cleat.
Bend – Joins two ropes.
Bitter End – End of a line
Dressing – Knot dressing is arranging a knot in such a way as to improve its performance.
Fast – Attaching a line using a knot.
Hitch – A hitch is a knot that attaches a rope to some object, often a ring, rail, spar, or post.
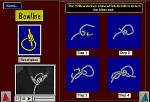
Loop knot – A loop knot is the type of knot that forms a fixed loop. The bowline is a common loop knot.
Make Fast – To make a line tight.
Marlinspike – A pointed metal tool used in rope work, specifically for splicing.
Slipped knot – A slipped knot is any knot that unties when an end is pulled.
Splicing – Splicing is a method of joining two ropes done by untwisting and then re-weaving the rope’s strands.
Standing end – The standing end (or standing part) of a rope is the part not active in knot tying.
Stopper Knot – A knot in the end of a rope.
Sailboat Handling
Beam Reach – When you are sailing 90 degrees across the wind.
Beating – Sailing towards the wind source, tacking.
Broad Reach – When you are sailing between a Beam Reach and a Run.
Close Hauled – Where the wind is from ahead. The closest a sailboat can sail is about 45 degrees into the wind.
Close Reach – When you are sailing slightly below Close-hauled.
Come About – Turning a sailboat into and through the wind, with the sails moving from one side to the other. Also known as tacking.
Course – A direction a boat is steered towards a destination.
Cunningham – A control line that tightens the luff of the sail.
Downwind – Away from the wind.
Ease – To let out a mainsheet or jibsheet (such as when adjusting a sail).
Easing Off – Letting the sail out until it starts to luff again, then pulling it in to the just the point at where the luff ceases.
Flaking – Folding the sail.
Heading Up – Pointing the bow of the boat into the direction of the wind. This is done by pushing the tiller towards the sail.
Heading Down – Pointing the bow of the boat away from the direction of the wind. This done by pulling the tiller away from the sail.
Heel – The sideways tipping of the boat due to the wind’s effect.
Hike, Hiking – When skipper and crew sit on the edge of the boat and lean out to balance it.
In Irons – When a boat is dead ahead into the wind and cannot move.
Jibe – To turn the boat downwind across the wind, with the sails moving from one side to the other.
Leeward – Away from the wind, downwind.
Luffing – The action of letting the sail out until it starts to flutter. When the sail luffs, the boat loses speed.
Outhaul – A control line that adjusts the tension along the foot of the mainsail, attached to the clew.
Pinching the sail – The action of pulling the sail in too far when trimming. With the sail pinched, the boat loses speed.
Point of Sail – Where the boat is in relation to the wind
Port – The left side of the boat
Reaching – Where the wind is from the side. Reaching is the fastest and most comfortable point of sailing.
Starboard – The right side of the boat
Running – Where the wind is from behind or astern.
Trimming the sail – The action of pulling the sail in from a luff until it stops fluttering.
Windward – Toward the wind, upwind.